- Prospector
- Bandit
- PEP 8 and black
- pylama
- mypy
- flake8
- pylint
- pycodestyle
- pydocstyle
- it is compliant with most of PEP 257
Consistency is key. A group of programmers all writing in different styles, using different design philosophies, and poor naming schemes and smelly code leave a lot of vulnerabilities undiscovered.
Prospector
from their website,
Prospector is a tool to analyse Python code and output information about errors, potential problems, convention violations and complexity.
It brings together the functionality of other Python analysis tools such as Pylint, pycodestyle, and McCabe complexity.
Install with pip install prospector
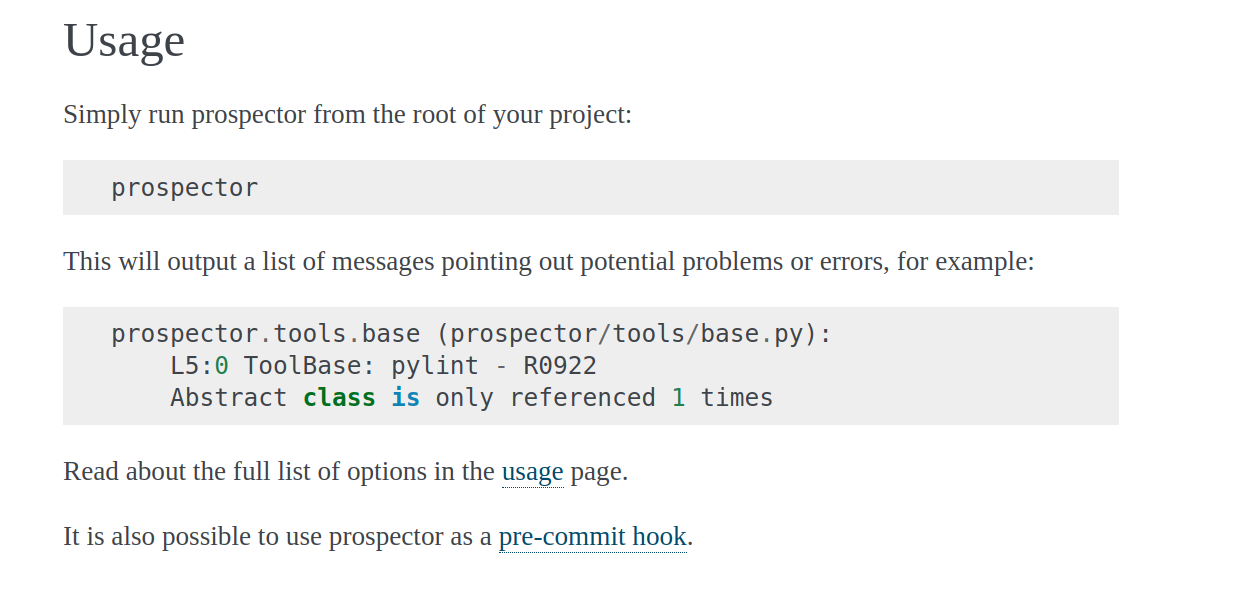 usage instructions from the project’s website
usage instructions from the project’s website
Running from the command line
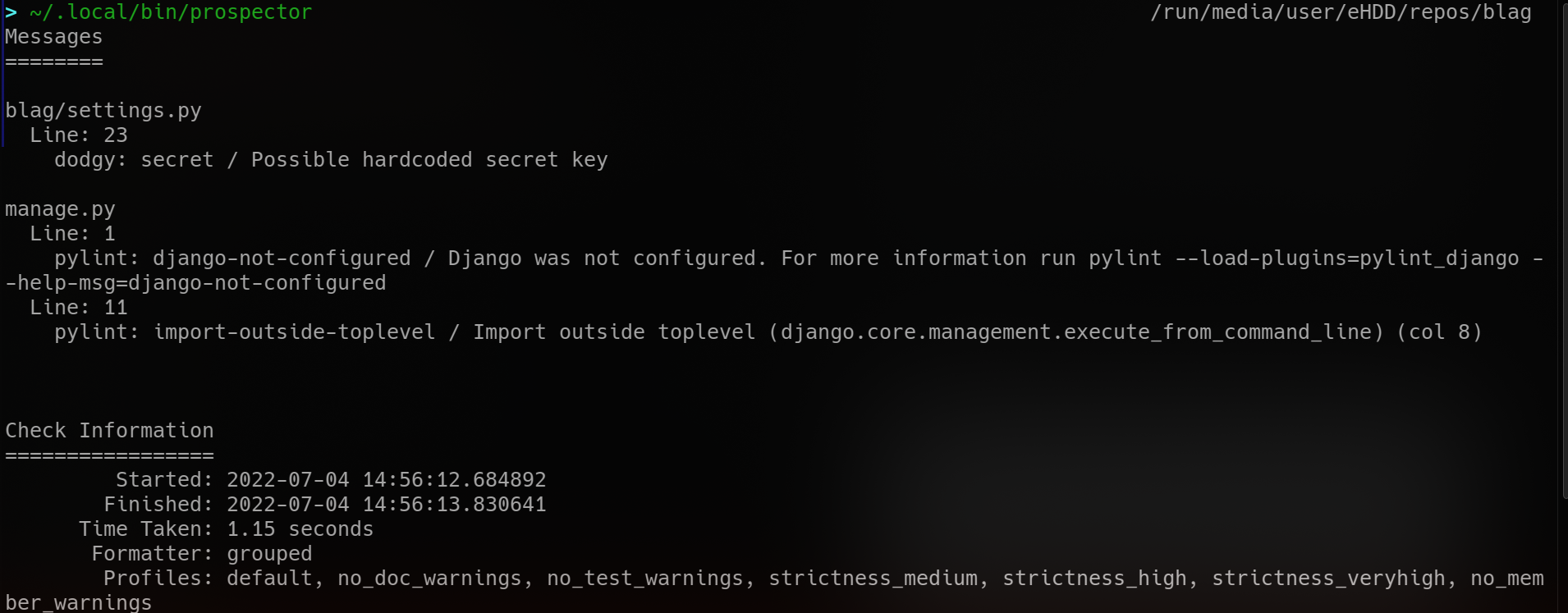 running prospector against a Django project
running prospector against a Django project
Recommended usage- On projects with a lower rate of commits, increase the strictness after every pass
prospector --strictness <level>
Valid levels are verylow, low, medium, high and veryhigh
This will ensure that the highest priority issues are addressed first, and AppSec moves down a list of warnings and errors, from high priority to low priority
Instead of running it on the commandline, you could integrate it into your development or CI/CD pipelines
For example, you can enable prospector linting in Visual Studio Code, and have it run on open files, project files, or all workspace files
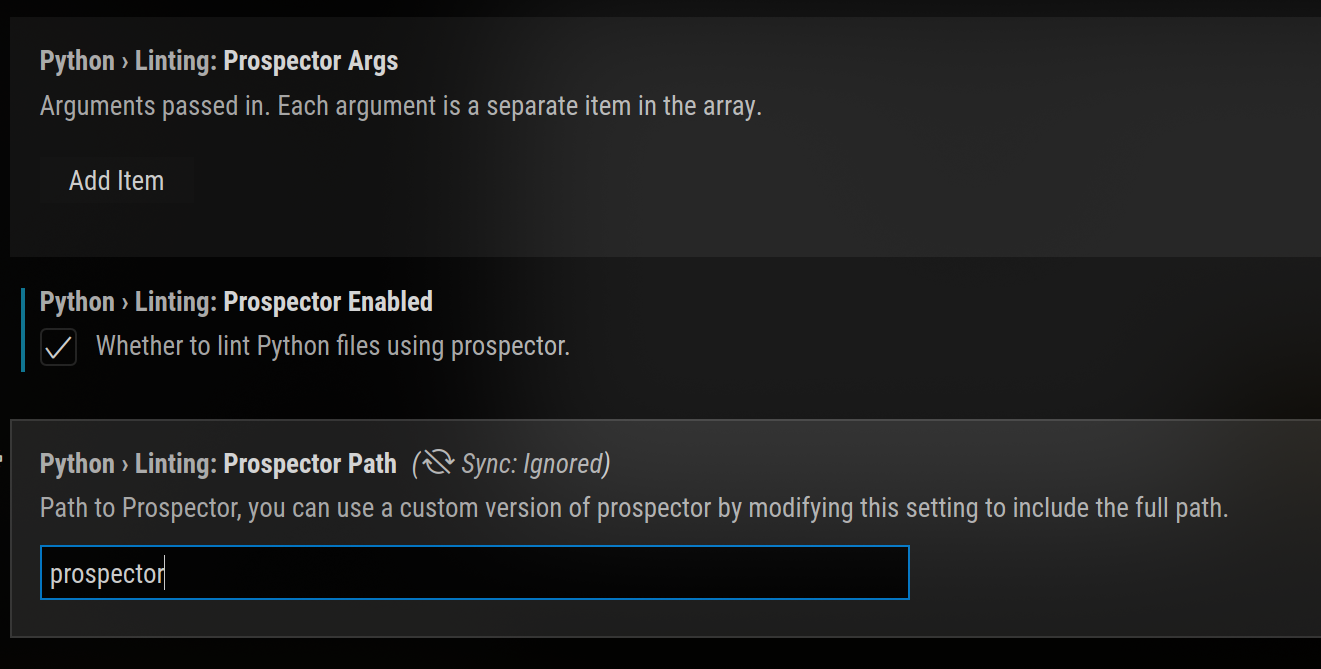 pass in your prospector args in Visual Studio Code
pass in your prospector args in Visual Studio Code
Bandit
a tool designed to find common security issues in Python code.
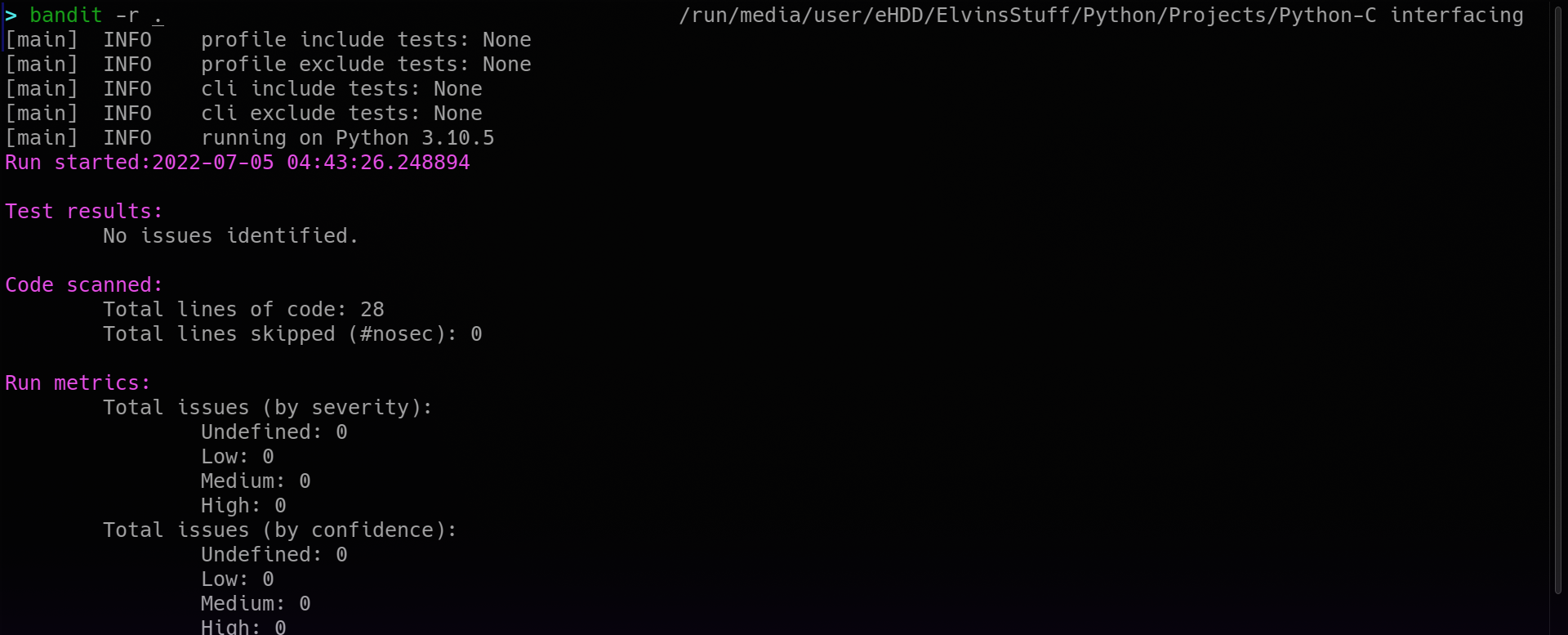 running bandit against a Python-C interfacing project
running bandit against a Python-C interfacing project
Bandit also has a pre-commit hook for version control integration
similar to Prospector, we can use a --severity-level {all,low,medium,high} switch
Add this to the pre-commit configuration
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit
rev: '' # Update me!
hooks:
- id: bandit
You can have your reports in a variety of file formats, listed here
Similarly, you can enable integration with many IDEs, for on-the-fly scanning
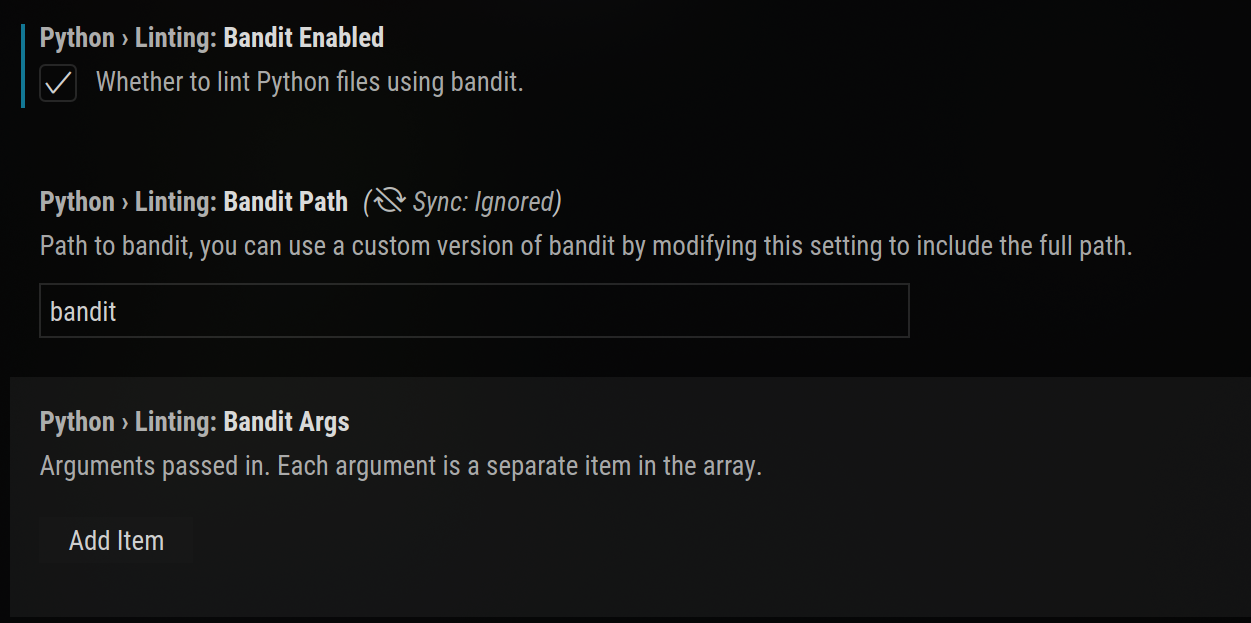 configuring Bandit integration in Visual Studio Code
configuring Bandit integration in Visual Studio Code
PEP 8 and black
PEP 8 is a style guide for python code. The guidelines cover indentation, tabs vs spaces, max. line length, blank lines, import statements, etc.
Black is a PEP 8 compliant opinionated formatter
Black reformats entire files in place. It intentionally has few configuration options so the developer can focus on the content instead.
You can choose to run it on directory(ies) or on file(s)
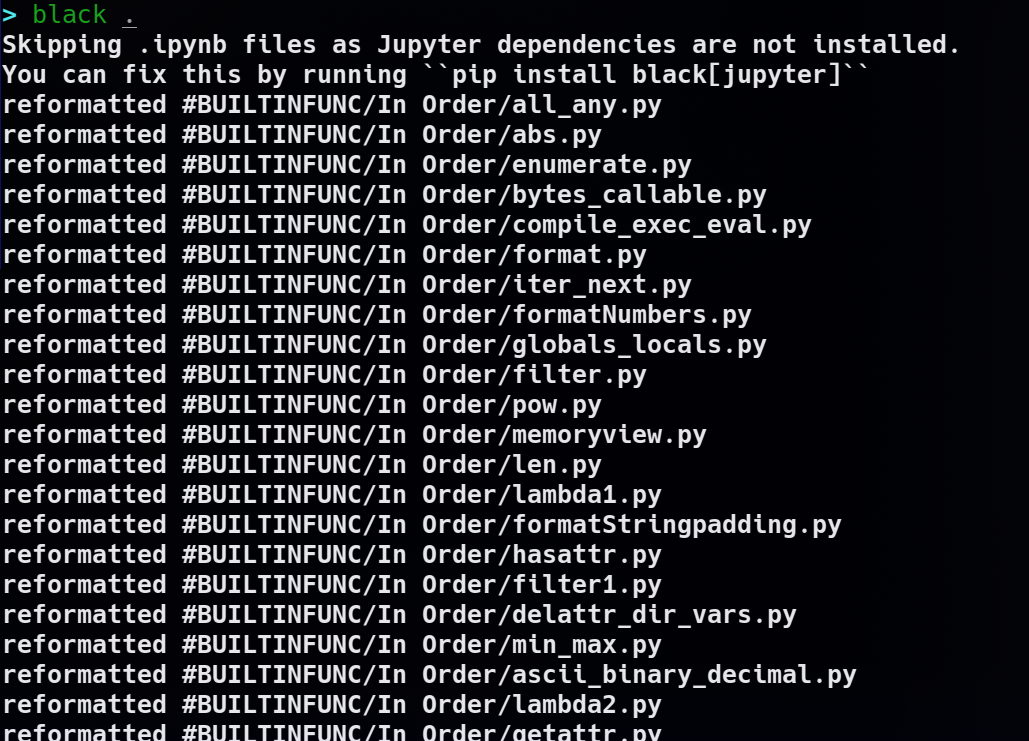 running black on a directory of Python scripts
running black on a directory of Python scripts
It is much easier to use, and has saner defaults compared to autopep8 and yapf
pylama
Code audit tool for Python. Pylama wraps these tools:
- pycodestyle
- pydocstyle
- Pylint
- Mypy
- eradicate
- Vulture
- PyFlakes
- Mccabe
- Radon
It is very easy to use, and does a lot of the heavy lifting for you. Invocation is simple, like most of the tools here.
mypy
Reasonably new versions of Python will have support for Type Hinting
PEP 484 introduced type hinting
From the Python docs,
The Python runtime does not enforce function and variable type annotations. They can be used by third party tools such as type checkers, IDEs, linters, etc.
The main goal is to write high-quality code which is easy to debug. Using a static type checker either through command line, on a file or project, or using the IDE integration
mypy is a static analyzer, when given code with type annotations, can type check your code and find common bugs
In an example I made here, the script runs without exceptions when given the test input list, but running mypy uncovers an issue- the returned variable can be a list of integers or None!
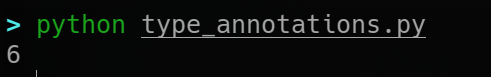 the script running without any errors
the script running without any errors
 running mypy on a python script, that exposes unseen issues
running mypy on a python script, that exposes unseen issues
flake8
A tool for style guide enforcement
Flake8 is configurable, and supports storing its configuration in your project in one of setup.cfg, tox.ini, or .flake8
flake8 --ignore D203 \
--exclude .git,__pycache__,docs/source/conf.py,old,build,dist \
--max-complexity 10
 running flake8 against a directory containing Python files
running flake8 against a directory containing Python files
Flake8 is a wrapper around pycodestyle
pylint
Pylint has a huge number of checks
Configuration can be stored in .pylintrc
pycodestyle
Check your Python code against some of the conventions in PEP8
Does not support variable name and docstring conventions, and does not apply fixes natively, but these can be enabled with plugins
pydocstyle
Documentation is very important!
Checks compliance with docstring conventions, to ensure the code can be understood and maintained by other parties