Aim
Studying Linux and Windows network commands. [ping, pathping, ipconfig/ifconfig, arp, netstat, nbtstat, nslookup, route, traceroute/tracert, nmap, etc]
GNU/Linux
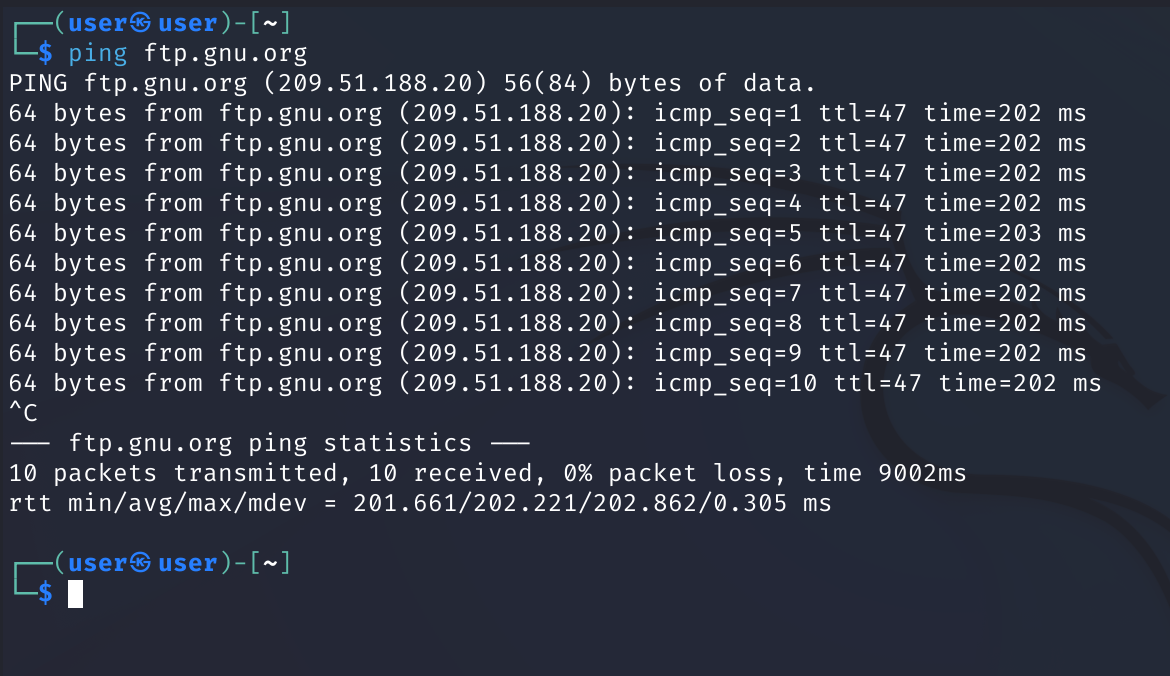
ping
Usage
ping [options] <destination>
ping uses ICMP datagrams to provoke a response from the chosen destination host, mainly intending to probe whether it is alive.
It sends ICMP ECHO_REQUEST to network hosts
Here, we use ping to check whether ftp.gnu.org is up, and to see how many packets were dropped, along with the time-to-response(latency)
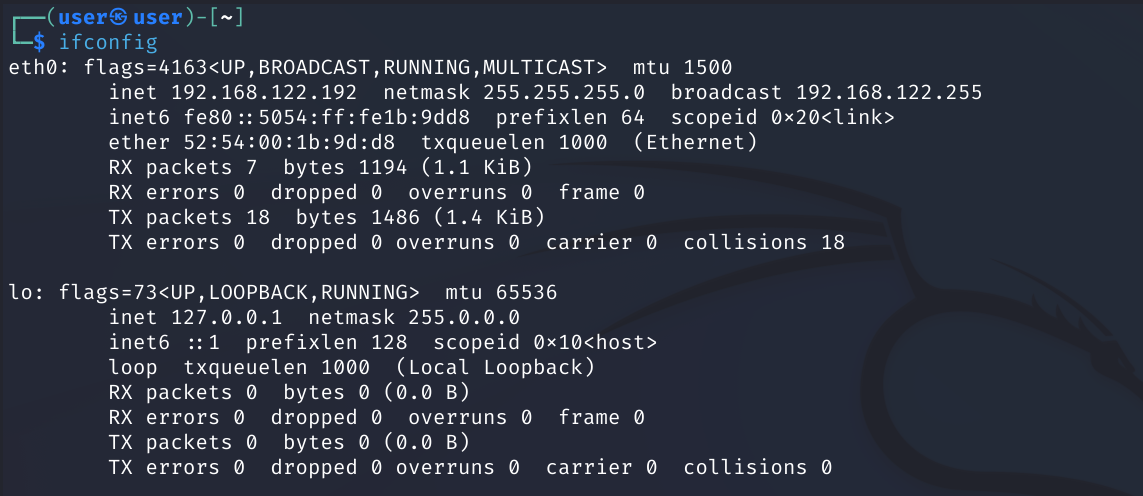
ifconfig
ifconfig is a program to retrieve and to set selected properties of
network interfaces.
Now, we’ll run only ifconfig to see a listing of all the network interfaces on this system
Here, we see the ethernet interface eth0 listed, with an IPv4 address of 192.168.122.192, with a netmask 255.255.255.0
We also see the MTU(Maximum transmission unit) defined
On the third line, we see the MAC address for this NIC
The second interface listed is a loopback interface. The most commonly used IP address on the loopback network is 127.0.0.1 for IPv4 and ::1 for IPv6. The standard domain name for the address is localhost.
arp
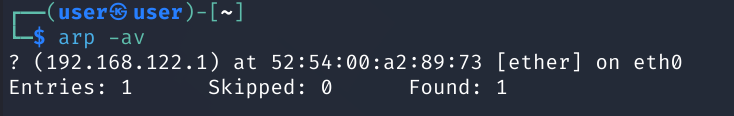
Use arp to manipulate the system’s ARP cache
arp manipulates or displays the kernel’s IPv4 network neighbour cache
You can add, delete or simply display the current contents of the cache
Here, we use the -a flag to use the BSD-style output format, and the -v flag to print verbose output
ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol, and is used to find the MAC address of a network neighbour for a given IPv4 address
netstat
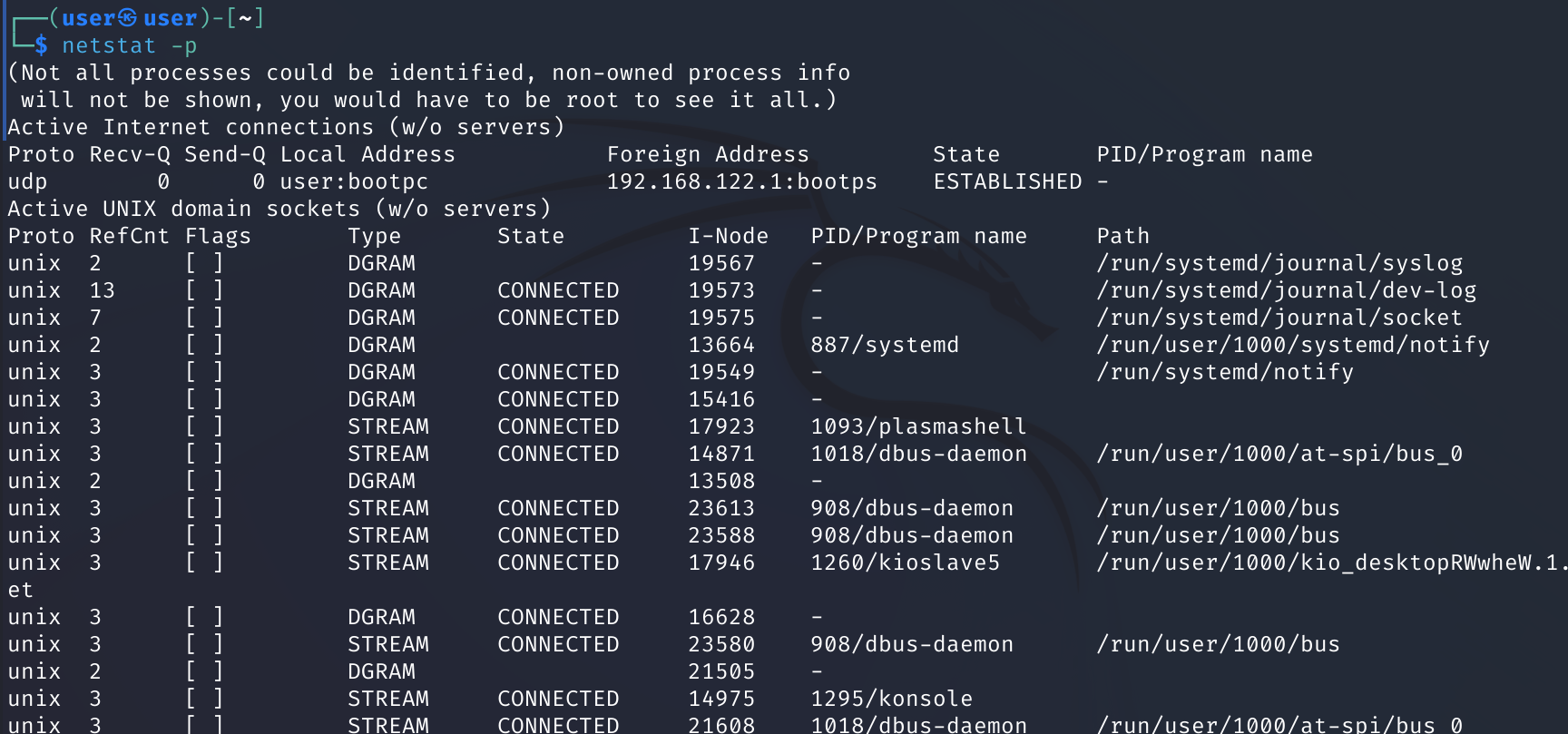
We can use netstat to print network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade connections, and multicast memberships.
Here, the -p flag is used, which shows the PID and name of the program to which each socket belongs
nslookup

nslookup is used to query internet nameservers interactively
Here, we will use the non-interactive mode.
We lookup goatse.cx using nameserver 8.8.4.4
route
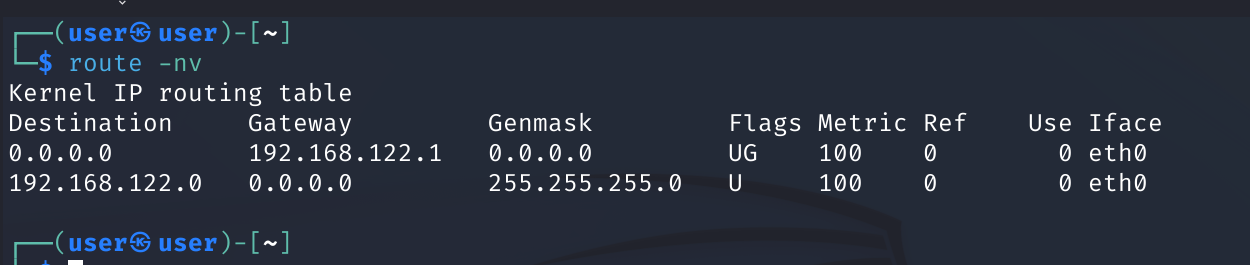
Use route to show or manipulate the IP routing table
We use the -n flag to show numerical addresse instead of trying to determine symbolic hostnames
The -v flag selects verbose operation
traceroute
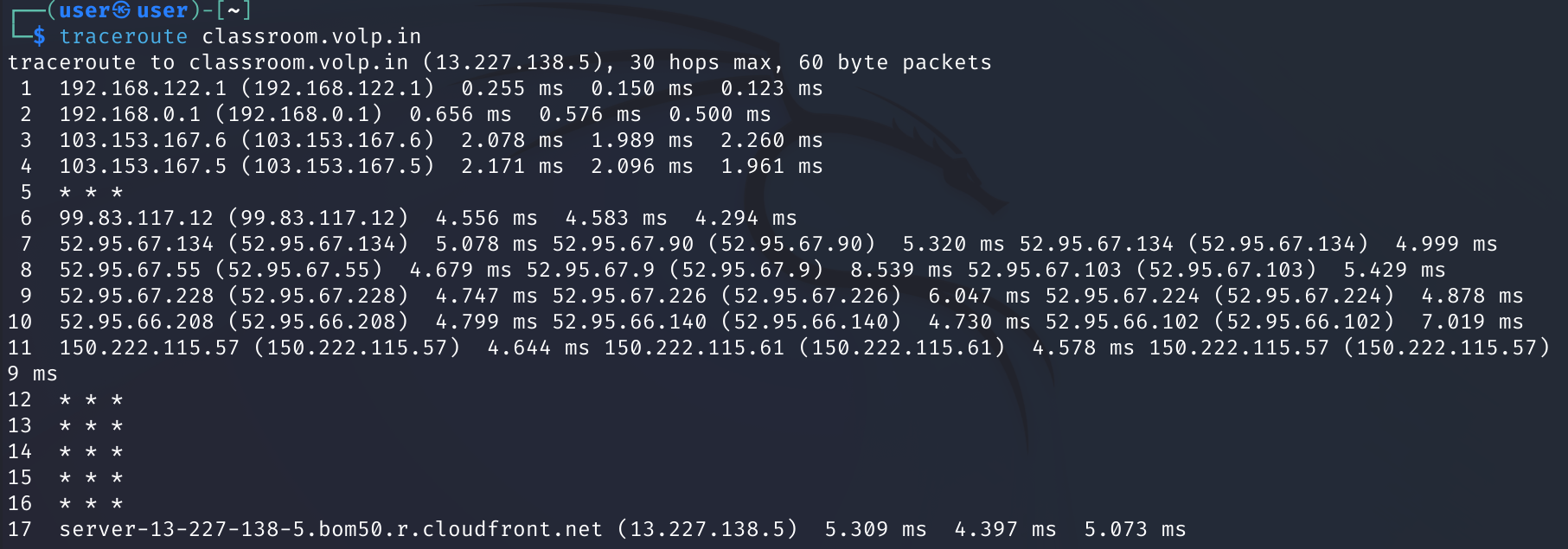
traceroute is used to print the route packets trace to a certain network host
Here, a simple traceroute is done to classroom.volp.in
The output shows every hop taken to the destination host, along with the time taken and resolved hostnames and IP addresses
There are many possible routes to a specific host, and this is evident from the command’s results
nmap
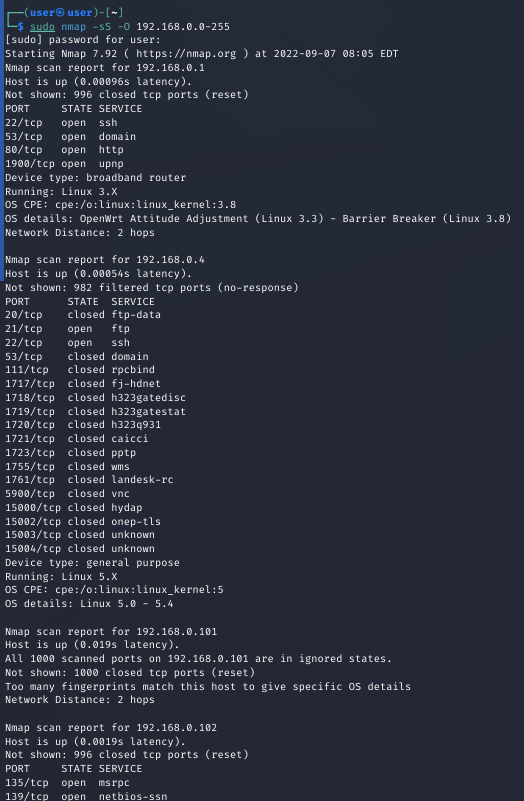
nmap is a network exploration tool and security/port scanner
It is an open source tool for network exploration and security auditing
Here, we invoke nmap and scan the network (hosts 192.168.0.0-192.168.0.255)
We use the -sS flag to perform a TCP SYN scan, which is fast, and can scan thousands of ports per second on a fast network. It is also relatively stealthy.
The -O flag enables remote OS detection using TCP/IP stack fingerprinting
The results of this scan show a list of hosts, their open ports, and a guess of the running operating system and also the device type
Microsoft Windows
ping
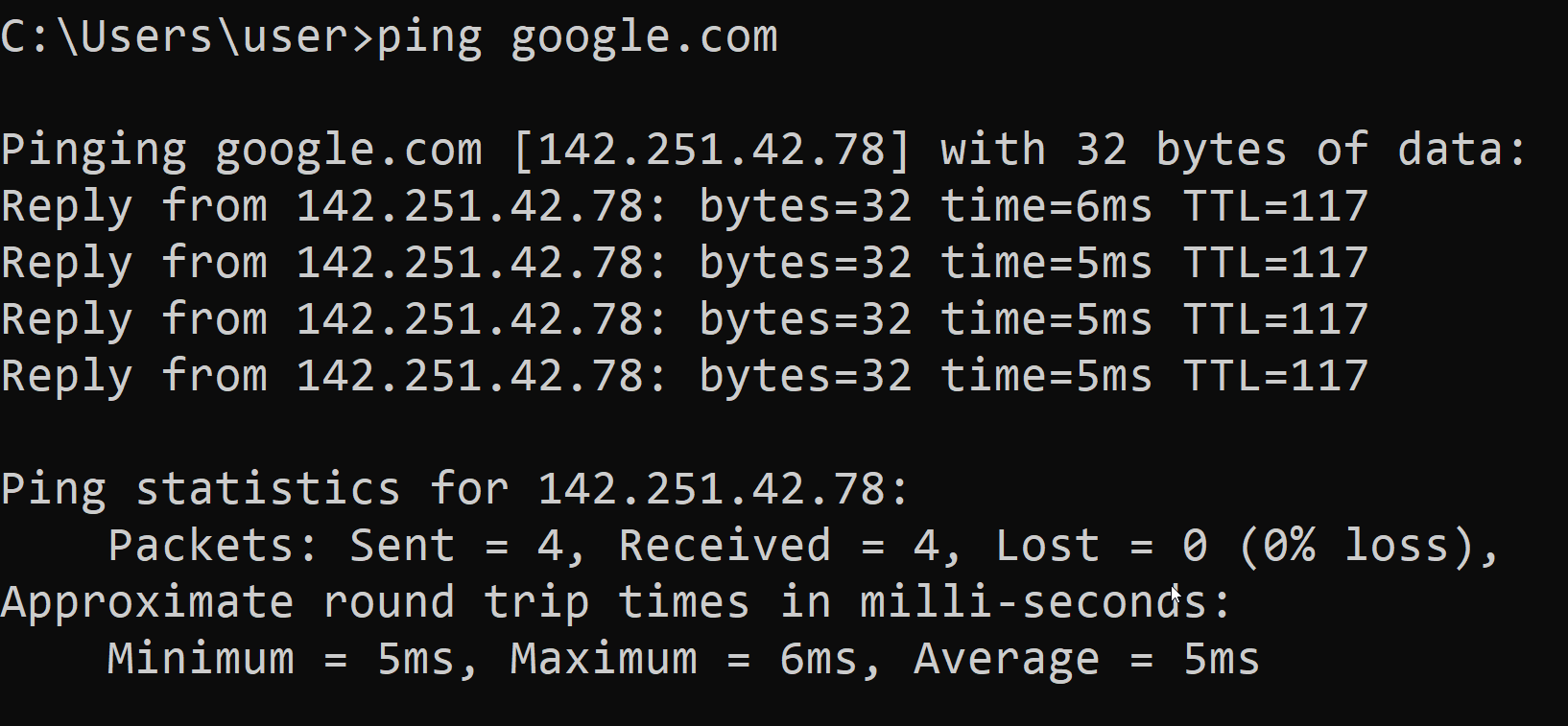
Usage:
ping [/t] [/a] [/n <count>] [/l <size>] [/f] [/I <TTL>] [/v <TOS>] [/r <count>] [/s <count>] [{/j <hostlist> | /k <hostlist>}] [/w <timeout>] [/R] [/S <Srcaddr>] [/4] [/6] <targetname>
ping verifies IP-level connectivity to another TCP/IP computer by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo Request messages
Here, we use ping to check whether google.com is up, and to see how many packets were dropped, along with the response time(latency)
pathping
Usage:
pathping [/n] [/h <maximumhops>] [/g <hostlist>] [/p <Period>] [/q <numqueries> [/w <timeout>] [/i <IPaddress>] [/4 <IPv4>] [/6 <IPv6>][<targetname>]
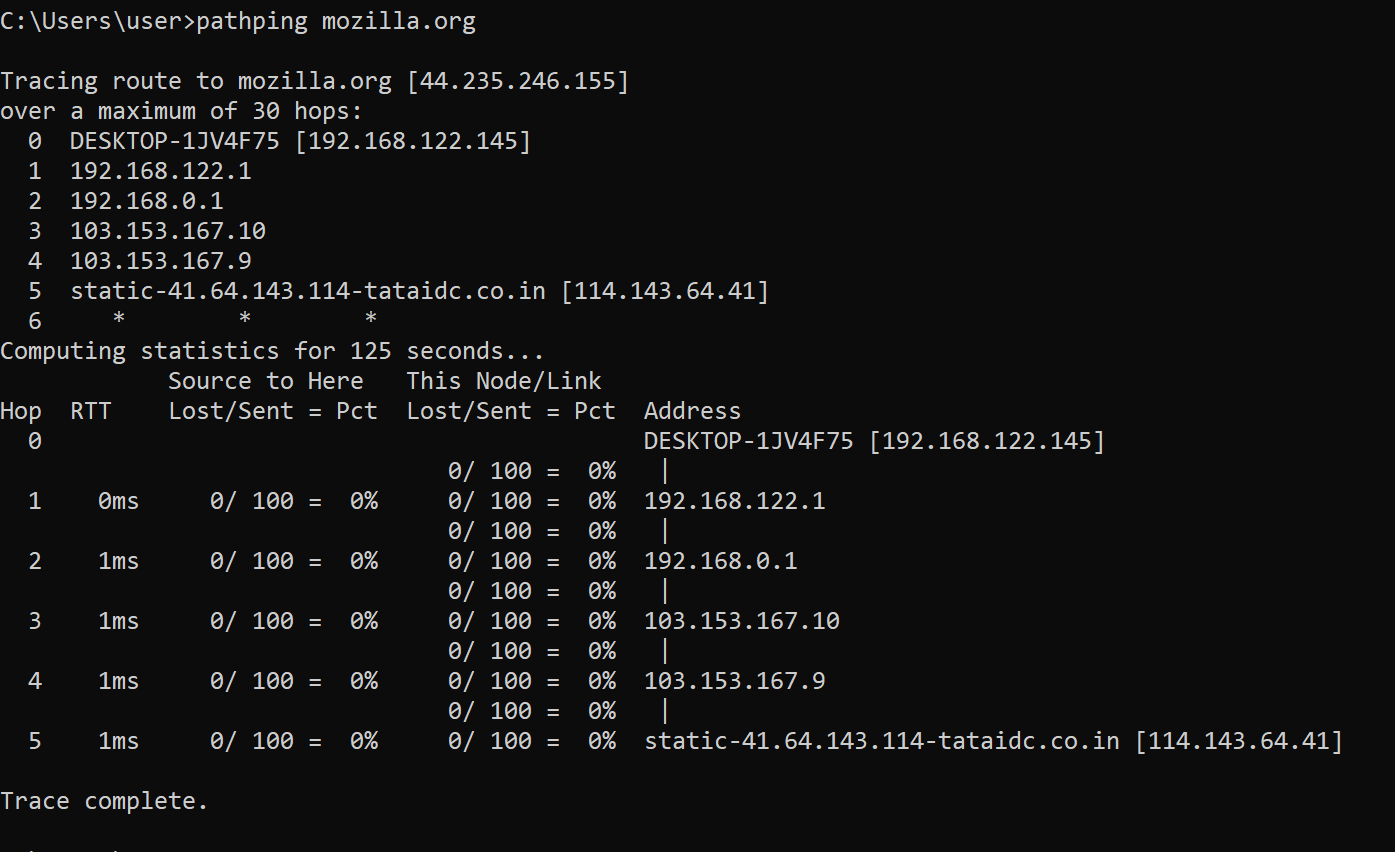
pathping provides information about network latency and network loss at intermediate hops between a source and destination
This command sends multiple echo Request messages to each router between a source and destination, over a period of time, and then computes results based on the packets returned from each router
Here, the destination is mozilla.org
ipconfig
Displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings network interfaces.
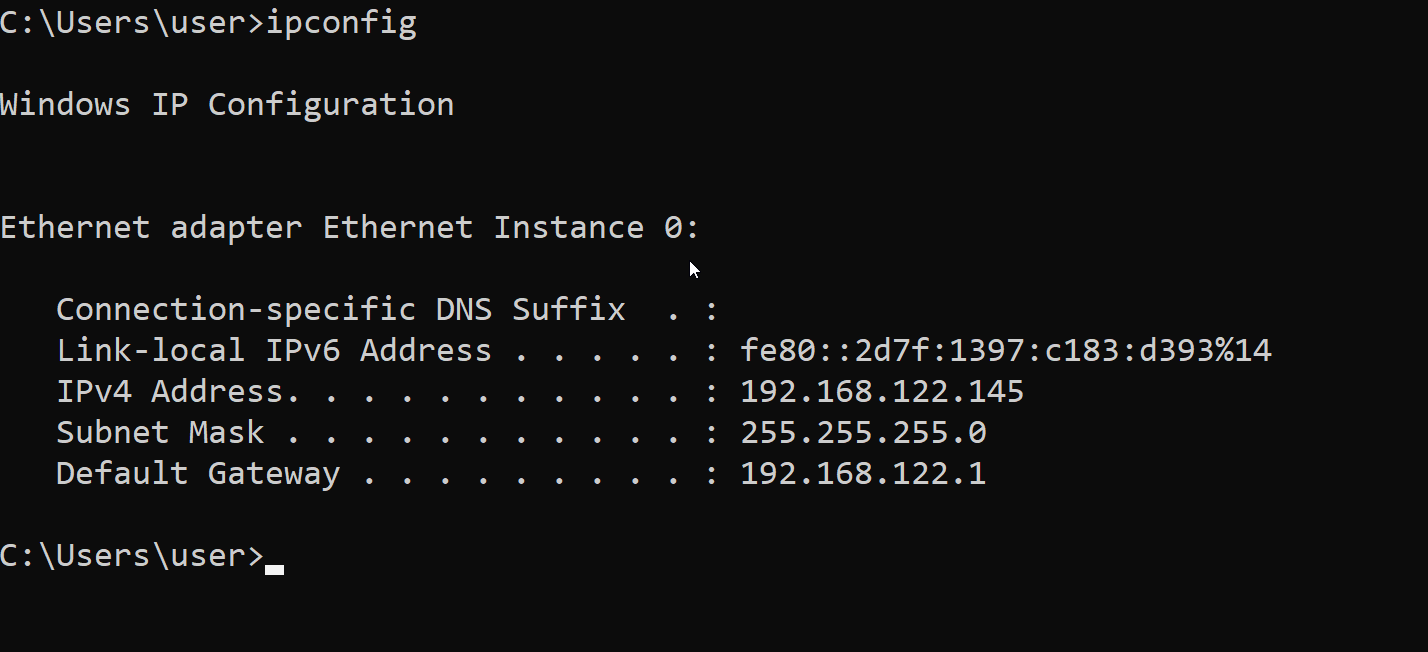
Now, we’ll run only ipconfig to see Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) and IPv6 addresses, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adapters
Here, we see the ethernet interface listed, with an IPv4 address of 192.168.122.145, with a netmask 255.255.255.0, and default gateway 192.168.122.1
arp
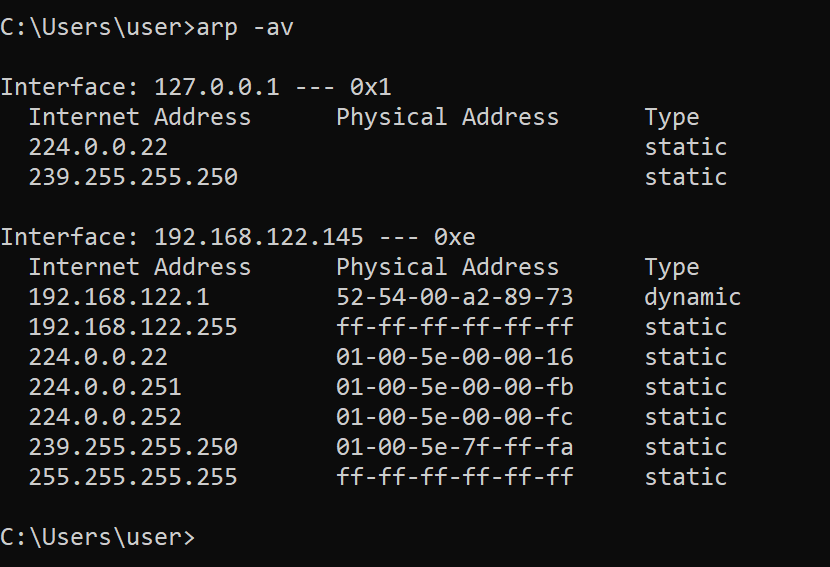
Displays and modifies entries in the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache
We use the -a flag to display current ARP table entries, and -v to enable verbose mode
nbtstat
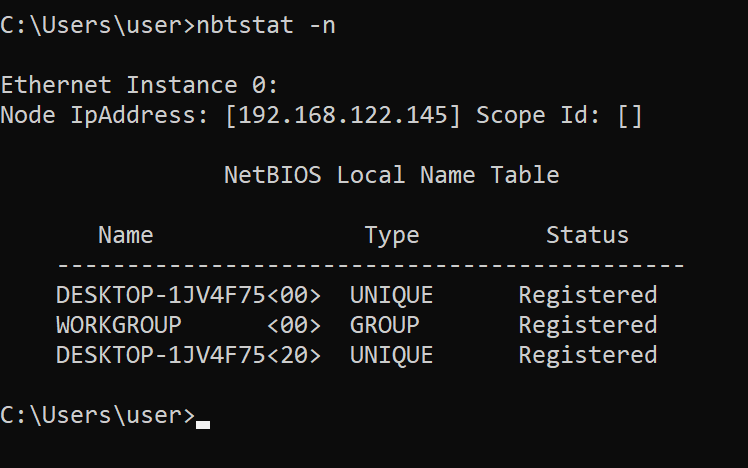
This tool displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP connections using NetBIOS over TCP/IP
The -n flag is used here, which lists local NetBIOS names
netstat
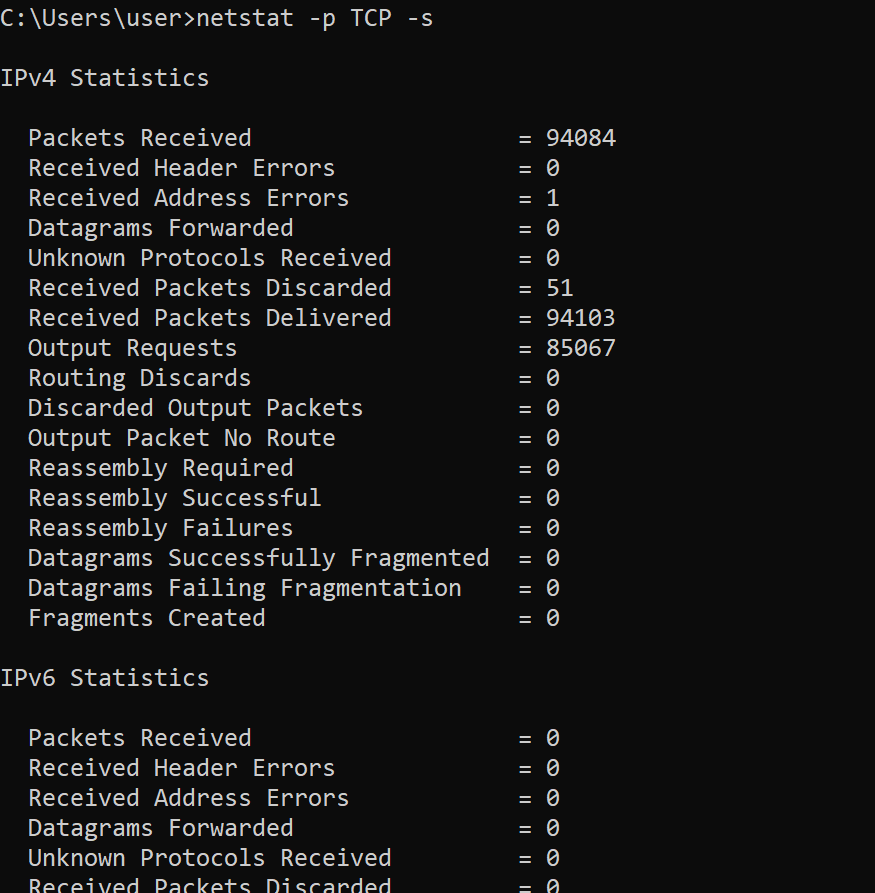
We can use netstat to print network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade connections, and multicast memberships.
Here, the -p flag is used with argument TCP to show connections of the TCP protocol
The -s flag shows per-protocol statistics
nslookup
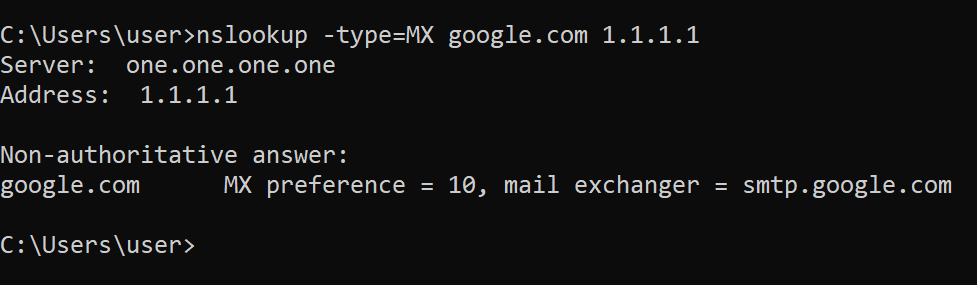
nslookup is used to query internet nameservers interactively
Here, we will use the non-interactive mode.
We look up google.com using nameserver 1.1.1.1
The -type flag with value of MX is used to set query type to MX records
route
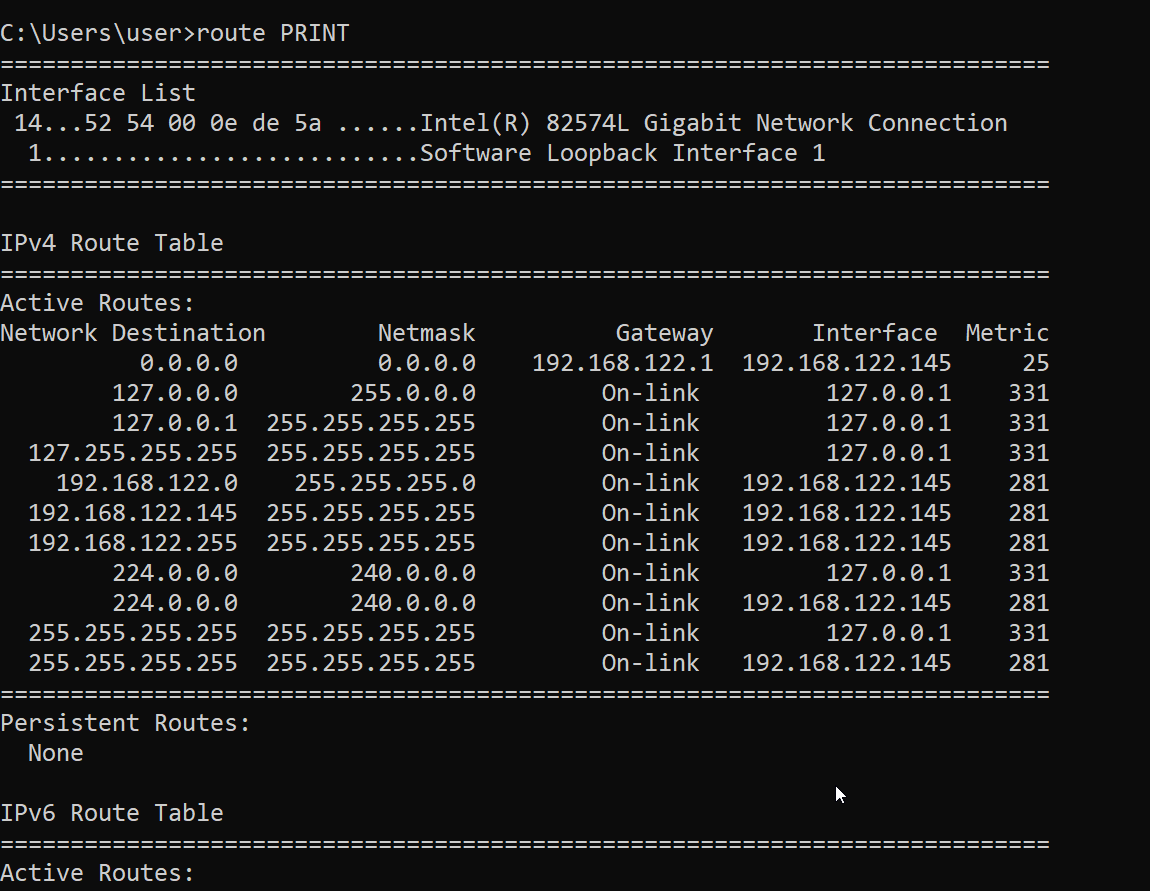
Use route to show or manipulate the IP routing table
The working is similar to the Linux command of the same name
tracert
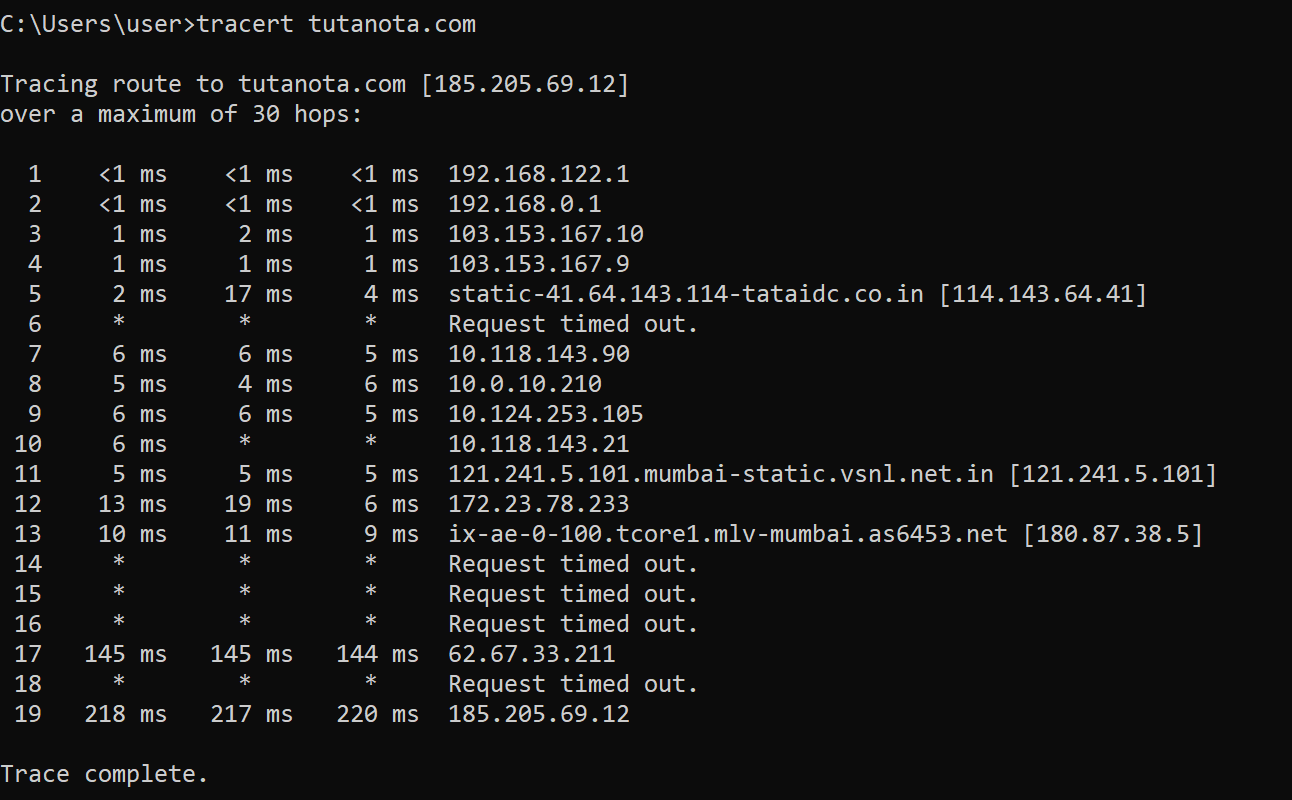
tracert determines the path taken to a destination by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo Request or ICMPv6 messages to the destination with incrementally increasing time to live (TTL) field values
Here, a simple tracert is done to tutanota.com
Some routers do not return time Exceeded messages for packets with expired TTL values and are invisible to the tracert command. In this case, a row of asterisks (*) is displayed for that hop
nmap
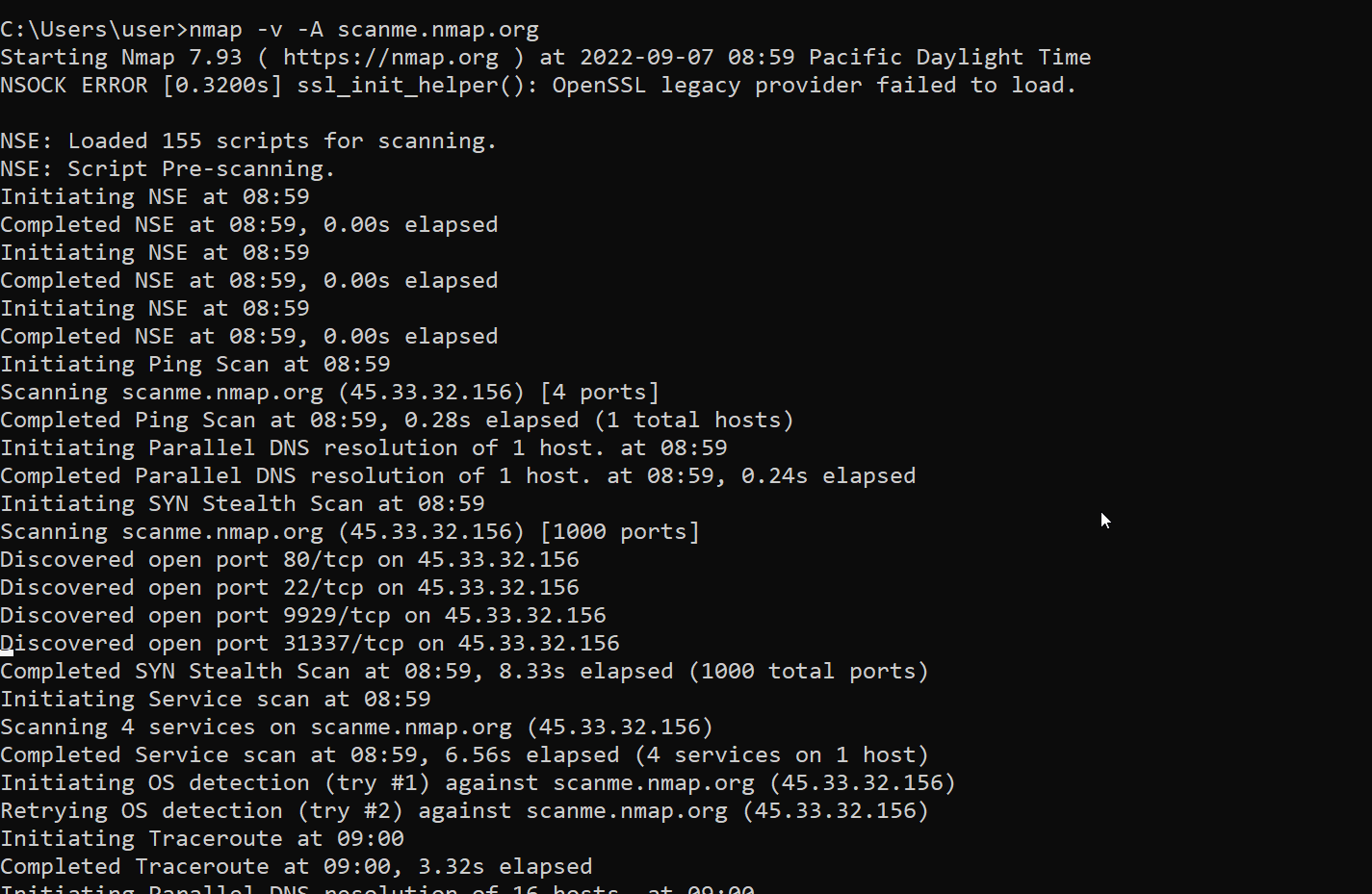
nmap is a network exploration tool and security/port scanner
The usage is the same as on GNU/Linux.
We use the -A flag to enable OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute
The -v flag enables verbose output
The target host is scanme.nmap.org
Conclusion
We have learned usage of the fundamental Linux and Microsoft Windows command-line tools.
Tools like ping and traceroute/tracert are fundamental in troubleshooting network connectivity issues. ipconfig is a commonly used to clear the DNS cache when issues with name resolution arise
We have also gained some insight into the internals of the Linux and Windows network stack, along with some networking protocols and concepts. Some examples include- sockets, routing tables, DNS and nameservers, IP addressing, TCP 3-way handshake, MAC addresses, loopback interfaces, MTU, ICMP, ARP
Lastly, some experience has been gained with the general syntax and usage of the command-line - usage of arguments, values, and flags to achieve a desired result. These results can be parsed with the programming language of our choice to incorporate logic, or to simply view the results as-is.