IP addressing
prereq reading
LAN and subnetting
Subnetting is achieved by splitting up the number of hosts that can fit within the network, represented by a number called a subnet mask.
Subnets use IP addresses in three different ways, to identify the
- network address
- host address
- default gateway
for small networks like a home network, you likely will not need more than 254 devices connected at a time
example of an assigned IP address(and subnet) of a computer on a small network
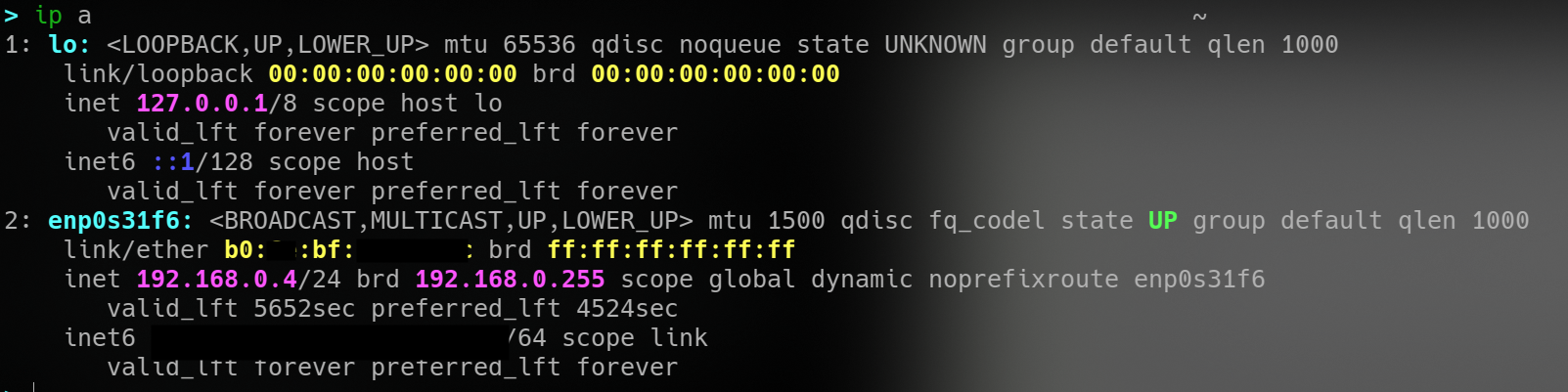
DHCP and DHCP Servers
IP addresses can be assigned manually, or automatically using a DHCP server
After connecting to a network, if not already assigned an IP address, a DHCP Discover request is sent out to check for DHCP servers on the network
the DHCP server then replies with an IP the device could use with a DHCP Offer
the client confirms by sending a DHCP Request
the DHCP server will send a DHCP ACK reply
MAC addresses
Each Network Interface Card has a (supposedly)unique MAC
It is a 12-character (hexadecimal numbers) address
the first 3 pairs identify the manufacturer and the other 3 are the “unique” address of the NIC
MAC addresses can be spoofed with programs like macchanger
ARP
associating MAC with IP
between layer 2 and 3 of the OSI model
allows devices to identify themselves on a network
